The eCommerce sector in Singapore continues to present enticing opportunities for entrepreneurs and brand owners. The combination of low entry barriers and the potential for substantial returns has sparked a surge of interest in online selling. However, with this opportunity comes the challenge of choosing the right platform to build and sustain a brand in an increasingly competitive market.
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process by comparing four leading eCommerce platforms: Amazon, Shopify, Lazada and Shopee. Our goal is to provide you with the insights needed to make an informed decision tailored to the unique characteristics of the Singapore market.

What Sets This Guide Apart?
1. Singapore-Centric Approach: Our analysis is specifically tailored to the Singapore market, taking into account local consumer habits, purchasing journeys, and market dynamics.
2. Expert Insights: We’ve combined our firsthand experiences of selling on various marketplaces with valuable input from eCommerce experts to provide a well-rounded perspective.
3. Addressing Real Concerns: This guide tackles common questions and doubts faced by brand owners, offering practical insights to help navigate challenges.
4. Comprehensive Platform Comparison: By including Amazon alongside Shopify, Lazada, and Shopee, we offer a more complete view of the options available to Singapore-based sellers.
5. Up-to-Date Information: With the latest 2024 updates and features incorporated, this guide ensures you’re making decisions based on current market conditions.
As we delve into the pros and cons of each platform, key considerations for choosing, and conclusions for new brand owners, our aim is to equip you with the knowledge needed to thrive in Singapore’s dynamic eCommerce ecosystem. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand your online presence, this guide will serve as a valuable resource in your eCommerce journey.
Pros & Cons of the 4 Platforms
Amazon: Pros and Cons
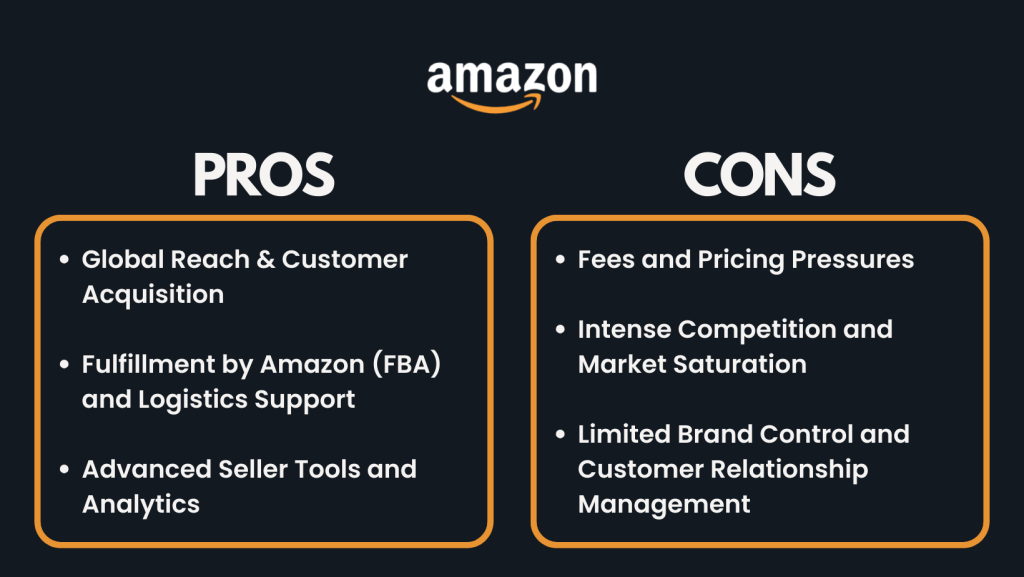
Pros
1. Global Reach & Customer Acquisition
Amazon’s vast global presence offers Singapore sellers unprecedented access to international markets. With nearly 2.4 billion monthly visits to its websites worldwide, Amazon provides an unparalleled platform for exposure and sales potential.
For Singapore-based businesses, this means:
- Exponential Growth Opportunities: Selling beyond Singapore’s limited market size (population: 5.9 million) into major global markets like the US, UK, and Germany. Access to a wide range of customers, including the significant expat population in Singapore (about 29% of the total population) who are already familiar with and trust Amazon.
- Year-Round Sales Potential: Ability to tap into various international shopping events and seasons, reducing dependence on local sales cycles. Amazon’s Global Selling program specifically supports international expansion, offering tools and guidance for cross-border trade. This can be particularly beneficial for Singapore sellers looking to establish a global brand presence.
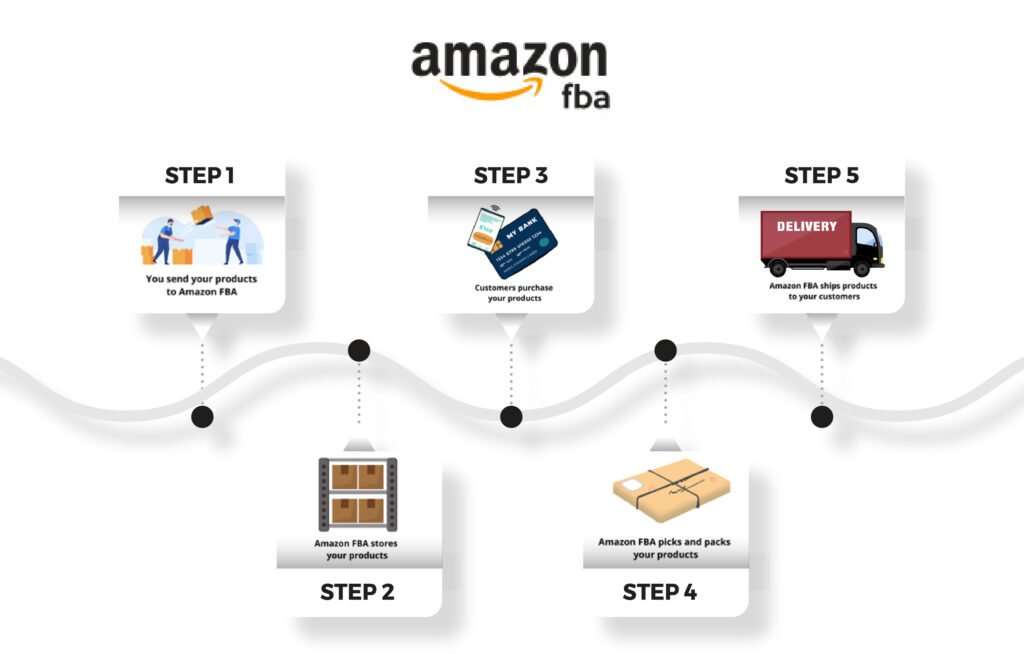
2. Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Logistics Support
Amazon’s robust fulfillment network, particularly through the Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program, provides Singapore sellers with a powerful logistics solution that can significantly streamline operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key benefits include:
- Global Distribution Network: Access to Amazon’s vast, efficient logistics infrastructure spanning multiple countries. This is particularly valuable for Singapore sellers, as it eliminates the need to establish individual shipping arrangements for different international markets.
- Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled by Amazon become eligible for Prime shipping, increasing their visibility and appeal to Amazon’s most loyal customer base. Prime members spend significantly more on Amazon compared to non-Prime customers.
- Customer Service and Returns Handling: Amazon manages customer inquiries and returns, reducing the operational burden on sellers. This is especially beneficial for Singapore-based businesses dealing with international customers across different time zones.
- Multi-Channel Fulfillment: FBA can be used to fulfill orders from other sales channels, including your own website, providing a centralized inventory management solution.
For Singapore sellers, FBA can effectively solve many of the challenges associated with international shipping and customer service, allowing them to compete on a level playing field with local sellers in various markets.
3. Advanced Seller Tools and Analytics
Amazon provides sellers with a suite of sophisticated tools and analytics that can significantly enhance business decision-making and operational efficiency. These tools are particularly valuable for Singapore sellers looking to understand and penetrate new markets.
Key features include:
- Seller Central: A comprehensive dashboard for managing your Amazon business, including inventory, orders, and performance metrics.
- Brand Analytics: Provides insights into customer search and purchase behavior, helping sellers optimize their product listings and marketing strategies.
- A+ Content: Allows brand-registered sellers to enhance product detail pages with rich media and detailed product information, improving conversion rates.
Additionally, third-party tools like Jungle Scout and Helium10 offer even more advanced analytics and research capabilities, including:
– Product research and trend analysis
– Keyword optimization
– Competitor tracking
– Profit calculation and inventory management
For Singapore sellers new to international markets, these tools provide crucial insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes in different countries. This data-driven approach can significantly reduce the risk and guesswork involved in expanding to new markets.
Cons
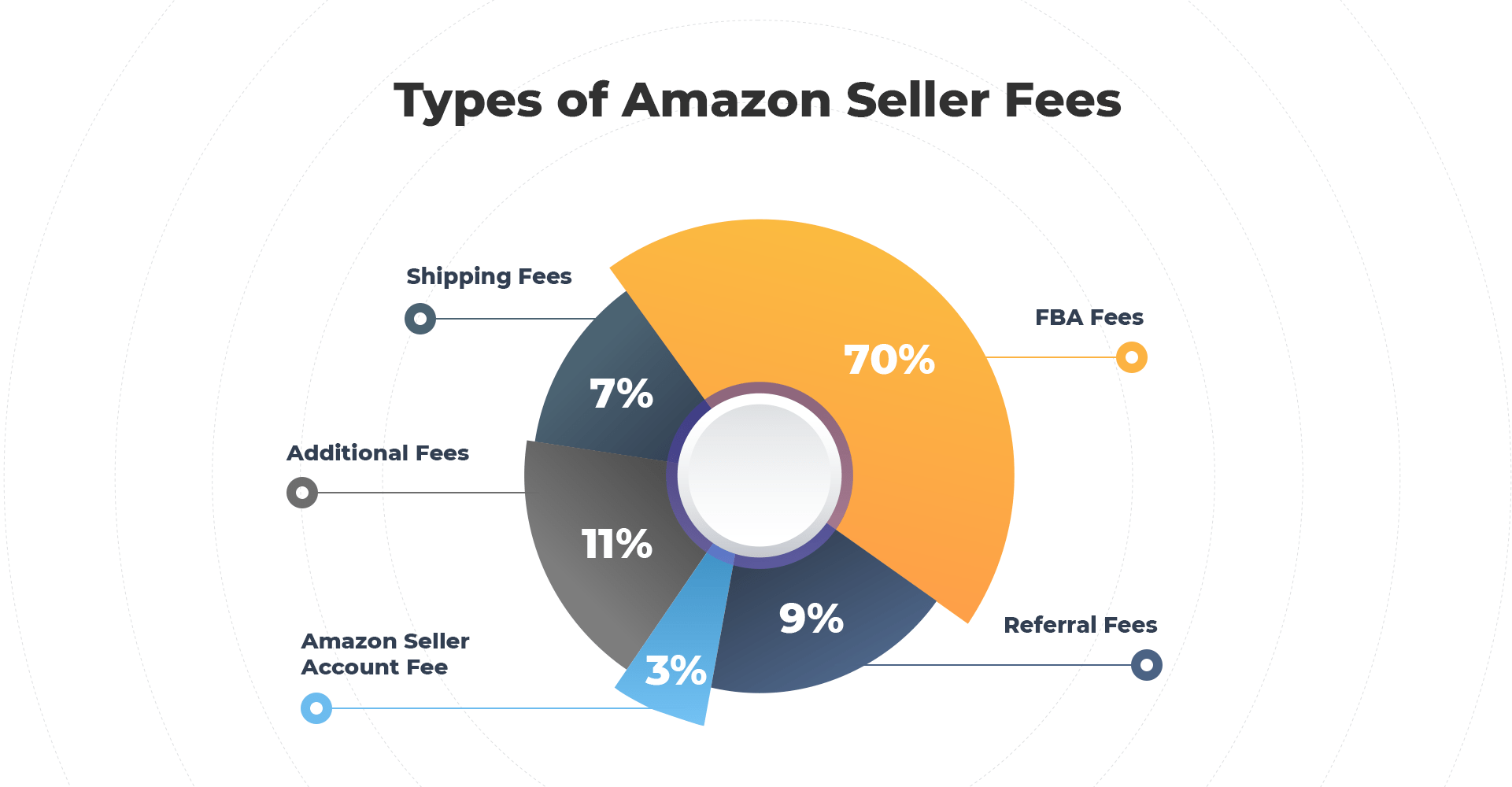
1. Fees and Pricing Pressures
While Amazon offers access to a vast customer base, it comes at a cost. The fee structure can be complex and potentially eat into profit margins, especially for sellers from Singapore who may face additional challenges due to international shipping and currency exchange rates.
Key considerations include:
- Referral Fees: Amazon charges a percentage of the sale price for each item sold. These fees vary by category and can range from 6% to 20% of the product’s selling price.
- FBA Fees: If using Fulfillment by Amazon, sellers incur additional fees for storage, fulfillment, and optional services. These fees can be substantial, especially for larger items or during peak seasons.
- Monthly Subscription: Professional sellers pay a $39.99 monthly fee, regardless of whether they make any sales.
- Currency Conversion: Singapore sellers dealing in foreign currencies may face additional costs and risks due to exchange rate fluctuations. Furthermore, the highly competitive nature of Amazon’s marketplace often leads to pricing pressures:
- Race to the Bottom: The visibility of competing offers can lead to price wars, potentially eroding profit margins. Many sellers use automated repricing tools, which can quickly drive prices down in competitive categories.
- Seasonal Fluctuations: Prices may need to be adjusted frequently to remain competitive during different shopping seasons and events.For Singapore sellers, it’s crucial to carefully calculate all potential fees and factor in international shipping costs when setting prices to ensure profitability while remaining competitive.
2. Intense Competition and Market Saturation
The flip side of Amazon’s massive customer base is the equally large number of sellers vying for attention. This intense competition can make it challenging for new or smaller Singapore-based sellers to gain visibility and market share.
Key challenges include:
- Global Competition: Singapore sellers aren’t just competing with local businesses, but with sellers from around the world, including large established brands and manufacturers. There’s also particularly strong competition from Chinese sellers who often have direct access to manufacturers and can offer very competitive prices. According to Marketplace Pulse, Chinese sellers account for a significant portion of top sellers on Amazon.
- Constant Optimization: Maintaining visibility requires ongoing effort in optimizing product listings, managing inventory, and adjusting prices. This can be time-consuming and may require dedicated resources.
- Advertising Costs: With organic visibility becoming increasingly difficult, many sellers find themselves relying heavily on Amazon’s advertising platform, Amazon Advertising, which adds to the overall cost of selling.
For Singapore sellers, this competitive landscape means:
– Higher customer acquisition costs
– Potential difficulty in establishing brand recognition
– Need for unique value propositions or niche products to stand out
It’s essential for Singapore sellers to conduct thorough market research and competitive analysis before entering specific product categories on Amazon.
3. Limited Brand Control and Customer Relationship Management
While Amazon provides access to a large customer base, it comes at the cost of limited control over brand experience and customer relationships. This can be particularly challenging for Singapore sellers looking to build a strong, distinctive brand identity.
Key limitations include:
- Standardized Listings: Amazon’s product detail pages follow a standardized format, limiting the ability to create a unique brand experience.
- Customer Data Restrictions: Amazon’s policies restrict sellers from using customer data for marketing purposes outside of Amazon. This makes it difficult to build a direct relationship with customers or retarget them through other channels.
- Communication Limitations: Amazon closely monitors and restricts communication between sellers and customers to prevent abuse. This can make it challenging to provide personalized customer service or follow up on sales.
- Platform Dependency: Success on Amazon can lead to over-reliance on the platform, making it difficult to transition customers to other sales channels.
For Singapore sellers, these limitations mean:
– Difficulty in differentiating from competitors based on brand experience
– Challenges in building a loyal customer base that extends beyond Amazon
– Limited ability to cross-sell or upsell products outside the Amazon ecosystem
To mitigate these issues, Singapore sellers may need to consider a multi-channel strategy, using Amazon as part of a broader e-commerce approach that includes other marketplaces or a branded website.
Expert Insights with Syed Asadulla, founder of Project e Agency, a full service Amazon Agency.
Q: As an Amazon Verified Ads Partner, what strategies or tools will he recommend for brands to effectively leverage Amazon’s advertising platform when expanding globally?
Amazon Advertising is a powerful Ads platform within Amazon that allows the Brands to reach their potential audience by keyword bidding, re-targeting, contextual targeting, look alike audience etc. The main campaign types offered by Amazon Ads are Sponsored Products, Sponsored Brands, Sponsored Display and Sponsored TV Ads. Some of the ad types are not available in all Amazon marketplaces, The full suite of Ad tools is currently available only in the Amazon US marketplace.
When brands are expanding globally via Amazon, it is critical to have an Amazon Ads strategy to ensure the brand launch is effective and they reach the ideal audience hence maximising conversions and brand awareness. Some of the strategies recommended for the brands launching in new marketplaces are:
- Clear goals: Having clear KPIs of Revenue, ROAS and profitability can help prepare sustainable strategies that fits the brands mission and resources.
- Understanding the local market: It is important to understand every Amazon marketplace has its local brands, consumer habits, pricing and trends. It is critical for brands to understand the local market and then position their products and ads accordingly to maximise the ROAS.
- Long tail keyword targeting: With this strategy the brands bid higher for keywords that are relevant and have more than three words. These keywords usually are considered as low hanging fruit that can help the brands to improve their keyword ranking with lower bids and better ROAS.
Amazon Advertising platform is sufficient for the new brands to start their ads journey on Amazon. The platform offers detailed analytics and portfolio functionality to structure the products and categories while advertising. There are advanced software’s that connect to the Amazon Ads account that can help brands to automate campaigns to some extent and at the same time provide better understanding of the campaign performance. Some of the best tools we recommend are Scale Insights, Teikametrics, Helium 10’s Adtomic.
Q: What are the most common challenges you’ve observed for brands entering the Amazon marketplace, and how does your agency approach overcoming these obstacles?
A: Amazon Seller central or Vendor central backend can be quite challenging for new sellers to understand and navigate on the platform. Some of the biggest challenges which we have seen the new to Amazon brands face are:
- Understanding Amazon’s pricing model: Amazon’s pricing model can be quite complex for new sellers to understand. It is crucial to understand all the costs involved to sell on the marketplace and then price the products accordingly.
- FBA Inventory Management: One of the reasons for Amazon’s global success is their FBA offering, where customers can have their products delivered in same or next day. Amazon has announced major updates in 2024 that makes it hard for sellers to understand the costs involved and at the same time maintaining the KPIs setup by Amazon.
- Buy Box: Amazon’s algorithm uses multiple data points to rank products on the search results and at the same time offering buy box to only one seller at a time. If there are multiple sellers for a product, the sellers need to understand that just by listing the product on Amazon they do not automatically get the buy box.

Shopify: Pros and Cons
Pros
1. Full Control and Brand Identity
Shopify offers Singapore sellers complete control over their online presence, allowing for a strong, unique brand identity – a crucial factor for long-term success in e-commerce.
Key advantages include:
- Customizable Storefront: Shopify’s themes and customization options allow brands to create a unique online store that perfectly reflects their identity. We personally use Themeforest as an alternative for equally beautiful but more cost-efficient themes. This level of customization is particularly valuable for brands looking to stand out in a crowded global market, differentiating themselves from being just another product on a marketplace platform.
- Direct Customer Relationships: Unlike marketplace models, Shopify enables direct communication with customers, fostering loyalty and repeat business. This is especially important for Singapore brands aiming to build a strong local and international customer base.
- SEO Optimization: Shopify provides built-in SEO tools and integrates with various SEO apps, allowing sellers to optimize their stores for both local and international search engines. This can significantly improve organic traffic and reduce reliance on paid advertising.
2. Versatile Sales Channels and Integrations
Shopify’s platform extends far beyond a standalone online store, offering Singapore sellers a versatile ecosystem of sales channels and integrations.
Key features include:
- Omnichannel Selling: Shopify integrates with numerous marketplaces and social media platforms, including Amazon, eBay, Facebook, and Instagram. This allows sellers to not only manage multiple sales channels from a single dashboard, but also sync their products automatically to the different marketplaces and social channels, maximizing reach and efficiency.
- Local Marketplace Integrations: Shopify offers integrations with popular Southeast Asian marketplaces like Shopee and Lazada, allowing Singapore sellers to tap into these platforms’ large customer bases while maintaining centralized inventory and order management. This is particularly important given the strong presence of these marketplaces in Singapore.
- Payment Gateway Flexibility: Shopify supports a wide range of payment gateways, including local options like PayNow and regional favorites like GrabPay. This flexibility ensures that Singapore sellers can offer preferred payment methods to both local and international customers. Other important local payment options include DBS PayLah! and support for major credit cards through gateways like Stripe.
- Logistics Integrations: Shopify integrates with numerous shipping providers, including local Singapore options like Ninja Van and Qxpress, as well as SingPost. This streamlines the fulfillment process for both domestic and international orders, which is crucial for Singapore’s position as a global trading hub.
This versatility allows Singapore sellers to create a truly omnichannel presence, meeting customers wherever they prefer to shop while maintaining centralized control over their business operations.
3. Scalability and Business Growth Tools
Shopify provides a robust platform that can scale with your business, offering tools and features that support growth from startup to enterprise level.
Key scalability features include:
- Tiered Plans: Shopify offers multiple plan levels, from Basic to Advanced and even Shopify Plus for enterprise-level businesses. This allows Singapore sellers to start small and upgrade as their business grows, without the need to migrate to a new platform.
- App Ecosystem: The Shopify App Store offers thousands of apps that can add functionality to your store, from marketing and SEO tools to inventory management and customer service solutions. This allows Singapore sellers to customize their store’s capabilities as their business needs evolve.
- Analytics and Reporting: Shopify provides comprehensive analytics to help sellers understand their business performance and make data-driven decisions. For Singapore sellers expanding internationally, these insights can be crucial in understanding new markets and customer behaviors.
- Shopify Capital: While currently not available in Singapore, Shopify Capital offers business loans in some markets, which could be a valuable resource for Singapore sellers as they expand into markets where this service is available.
The scalability of Shopify makes it an attractive option for ambitious Singapore sellers looking to grow their business both locally and internationally over time.
Cons
1. Higher Setup and Maintenance Costs
While Shopify offers significant benefits, it comes with higher upfront and ongoing costs compared to marketplace selling, which can be challenging for new or small-scale Singapore sellers.
Key cost considerations include:
- Subscription Fees: Shopify’s plans range from SGD 39 to SGD 399 per month, with additional costs for advanced features. This recurring cost exists regardless of sales volume, which can be burdensome for new businesses.
- Transaction Fees: While Shopify Payments has no transaction fees, using external payment gateways incurs additional fees of 0.5% to 2% depending on your plan. For Singapore sellers using local payment gateways, these fees can add up.
- App Costs: Many essential or advanced features require third-party apps, which often have their own subscription costs. Popular apps can range from $10 to $100+ per month, quickly increasing overall expenses.
- Design and Development: Creating a professional, branded store often requires investment in custom design and development work. According to Shopify experts, custom theme development can cost anywhere from $3,000 to $100,000 or more.
For Singapore sellers, especially those just starting out, these costs can represent a significant investment compared to the relatively low entry costs of marketplace selling. If you are looking for an affordable Shopify developer, rates at Soodo start from $1200.
2. Marketing and Traffic Generation Challenges
Unlike marketplaces with built-in audiences, Shopify stores require significant effort and investment in marketing to drive traffic and sales.
Key challenges include:
- SEO Competition: While Shopify provides good SEO tools, competing for organic search traffic can be difficult, especially for new stores. Shopify-based sellers may find themselves up against established global brands with larger SEO budgets. This requires optimizing for brand-specific search terms and trends.
- Paid Advertising Costs: Many Shopify store owners rely heavily on paid advertising platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads. The cost per click in Singapore can be high, with average CPCs ranging from $1 to $2 or more, depending on the industry.
- Content Marketing Requirements: Successful Shopify stores often need to invest in content marketing, including blogs, social media, and email campaigns. This requires significant time and potentially the cost of hiring content creators. Singapore sellers need to tailor their content to local cultural nuances and holidays.
- Brand Building from Scratch: Without the trust factor that comes with selling on established marketplaces, Shopify store owners need to build brand credibility independently. This can be a slow and resource-intensive process.
- Competition with Local Marketplaces: Singapore has a strong presence of local and regional marketplaces like Lazada, Shopee, and Amazon. Shopify sellers in Singapore often need to develop strategies to compete with these established platforms or consider using Shopify’s multichannel capabilities to sell on these marketplaces in addition to their own store.
For Singapore sellers used to the built-in traffic of marketplaces, the shift to driving their own traffic can be a significant challenge and learning curve. If you are brand-building, we recommend the combination strategy of having presence in marketplace and your own store in the initial stages.
3. Technical Skills and Resource Requirements
Running a Shopify store requires a broader set of skills and resources compared to selling on marketplaces, which can be challenging for some Singapore sellers.
Key skill and resource requirements include:
- Web Design and Development: While Shopify is user-friendly, creating a professional-looking store often requires some design and development skills. According to Shopify, building a basic store can take 2-3 weeks, while a custom store can take 2-3 months. Our own experience at Soodo aligns with this timeline for new websites, while optimization of an existing store can take just 1-2 weeks.
- E-commerce Management: Store owners need to manage inventory, process orders, handle customer service, and more. This can be time-consuming and may require hiring additional staff.
- Digital Marketing Skills: Success on Shopify often requires proficiency in various digital marketing channels, including SEO, social media marketing, email marketing, and paid advertising. Singapore sellers need to focus on platforms popular in Singapore, such as WhatsApp, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Analytics and Data Analysis: To make informed business decisions, store owners need to be comfortable with data analysis, using tools like Google Analytics and Shopify’s built-in analytics.
- Continuous Learning: E-commerce and digital marketing best practices evolve rapidly. Store owners need to continually educate themselves to stay competitive. Shopify offers resources like the Shopify Academy, but keeping up can be time-consuming.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Singapore sellers need to ensure their stores comply with local e-commerce regulations:
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Sellers need to manage GST collection and reporting, which may require additional apps or integrations.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): While Shopify’s privacy features help, sellers need to ensure their data collection and usage practices comply with Singapore’s PDPA.
For Singapore sellers transitioning from marketplaces or starting their first e-commerce venture, acquiring these skills or hiring professionals with these skills can represent a significant investment of time and resources.
In conclusion, while Shopify offers powerful tools and flexibility for Singapore sellers, it also comes with unique challenges and requirements. Success on the platform requires careful consideration of these factors and a willingness to invest time and resources into building a strong, independent online presence.

Lazada: Pros and Cons
Pros
1. Expansive Market Reach and Strong Platform Backing
Lazada offers Singapore sellers access to a vast customer base, both locally and across Southeast Asia, backed by the technological prowess of Alibaba Group.
- Broad Customer Base: Access to millions of customers across Southeast Asia, including Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam. In Singapore alone, Lazada reported over 1.5 million monthly active users in 2021, according to Statista.
- Strong Backing and Technological Advancements: Supported by Alibaba Group, enhancing platform reliability and continuous investment in technological advancements. Alibaba’s expertise in e-commerce provides sellers with cutting-edge tools and features, such as AI-driven product recommendation engines and advanced analytics.
- Cross-Border Opportunities: Singapore sellers can easily tap into other Southeast Asian markets through Lazada’s cross-border selling program. This is particularly advantageous for Singapore’s strategic position as a regional hub, allowing local businesses to scale across borders efficiently. The platform handles currency conversions and provides localization support, making it easier for Singapore sellers to adapt to different markets.
2. Comprehensive Logistics Solutions and Operational Support
Lazada provides end-to-end logistics support and operational tools, crucial for efficient operations in Singapore and across Southeast Asia.
- Lazada Logistics and Fulfilment by Lazada (FBL): Offers end-to-end logistics solutions, including warehousing, packaging, and delivery. FBL, similar to Amazon’s FBA, manages storage, packaging, and delivery, allowing Singapore sellers to focus on product development and marketing rather than logistics.
- Operational Tools and Support: Seller Center provides a user-friendly platform for managing listings, orders, and analytics. Real-time data and performance metrics help Singapore sellers make informed decisions. Lazada University offers training and resources specific to selling in Singapore and Southeast Asia, providing insights into local consumer behavior and market trends. Dedicated local support team assists Singapore sellers in navigating local regulations and platform policies.
- Flexible Payment Options: Supports Singapore-specific options like PayNow and local bank transfers. Integrates with popular Southeast Asian payment methods, facilitating regional sales. Offers installment payment plans, which can increase conversion rates for higher-priced items.
3. Robust Marketing and Sales Tools
Lazada provides a range of marketing tools to help Singapore sellers increase visibility and sales, crucial in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
- Premium Brand Positioning and Advertising: LazMall offers a premium space for authentic brands and authorized distributors, helping Singapore sellers differentiate from general marketplace sellers and build brand trust.
- Sponsored Search and Display Ads allow sellers to increase product visibility through targeted advertising, particularly useful in Singapore’s competitive e-commerce landscape. The platform’s algorithm favors sellers who actively engage in promotions and maintain good performance metrics, incentivizing consistent effort.
- Campaign Tools and Sales Events: Provides tools for creating and managing sales campaigns, flash sales, and promotions. Aligns well with Singapore’s sales-driven shopping culture (e.g., Great Singapore Sale, 11.11 sales). Lazada’s big sale events like 11.11 and 12.12 offer massive exposure, though they require careful planning and often steep discounts.
Cons
1. Intense Competition and Pricing Pressure
The popularity of Lazada in Singapore results in a highly competitive environment that can challenge sellers’ profitability and visibility.
- High Seller Density and Price Wars: Singapore’s savvy shoppers often use Lazada and Shopee for price comparisons, putting significant pressure on profit margins. Some sellers engage in unsustainable price-cutting, creating a “race to the bottom” that can be challenging for Singapore sellers focusing on quality over price.
- Continuous Investment Required: Need for ongoing spending on advertising and promotions to maintain visibility. Can be costly, especially for small Singapore businesses or new entrants. During major shopping events like 11.11, the cost of advertising can skyrocket, potentially eating into profits.
- Challenges for Niche Products: The platform’s mass-market focus can make it difficult for niche or specialty products to gain traction. Singapore sellers with unique or high-end products may struggle to communicate their value proposition effectively within the platform’s standardized format.
2. Limited Customization and Brand Control
Lazada’s standardized platform can restrict brand expression and control, which can be particularly challenging for Singapore brands looking to create a unique identity.
- Restrictive Storefront Design and Brand Presentation: Limited ability to customize the look and feel of the online store. Can be challenging for Singapore brands looking to create a unique brand experience or maintain consistent branding across different sales channels. The standardized product listing format may not adequately showcase unique product features or brand stories.
- Platform Dependency and Policy Changes: Sellers are subject to Lazada’s policies and changes, which can sometimes be abrupt or unfavorable. Updates to algorithms or policies can impact a seller’s performance unexpectedly, requiring quick adaptation. The platform may prioritize its own interests over those of individual sellers, potentially affecting visibility or sales.
- Customer Relationship Limitations: Direct communication with customers is restricted to protect buyer privacy. Can be challenging for Singapore businesses used to building personal relationships with customers. Limited ability to re-market to past customers or build a direct mailing list, hindering long-term customer relationship building.
3. Financial Considerations and Operational Challenges
While Lazada provides access to a large market, it comes with financial implications and operational challenges that Singapore sellers need to navigate carefully.
- Fee Structure and Profitability Challenges: Commission fees (latest update as at May 2024) vary by category, typically ranging from 2% to 9% in Singapore. Additional payment processing fees for certain payment methods can further impact margins. The need for competitive pricing, coupled with these fees, can significantly squeeze profit margins, especially for low-margin products.
- Cash Flow Management: Lazada typically holds payments for a period before releasing them to sellers, which can impact cash flow. During sales events, the high volume of orders coupled with payment holds can create cash flow challenges, particularly for smaller Singapore businesses.
- Product Limitations and Approval Process: Certain categories (e.g., food, supplements) require additional approvals, which can be time-consuming and complex. Some products popular in Singapore may not be allowed on the platform, limiting opportunities for certain businesses. New sellers and products often go through a verification process, which can delay time-to-market for new products or seasonal items.
In conclusion, Lazada offers Singapore sellers a powerful platform to reach a wide audience across Southeast Asia, backed by robust logistics and marketing tools. However, success on the platform requires navigating intense competition, adapting to platform limitations, and carefully managing financials and operations. Sellers must weigh these factors against their specific business goals and resources to determine if Lazada is the right fit for their e-commerce strategy.
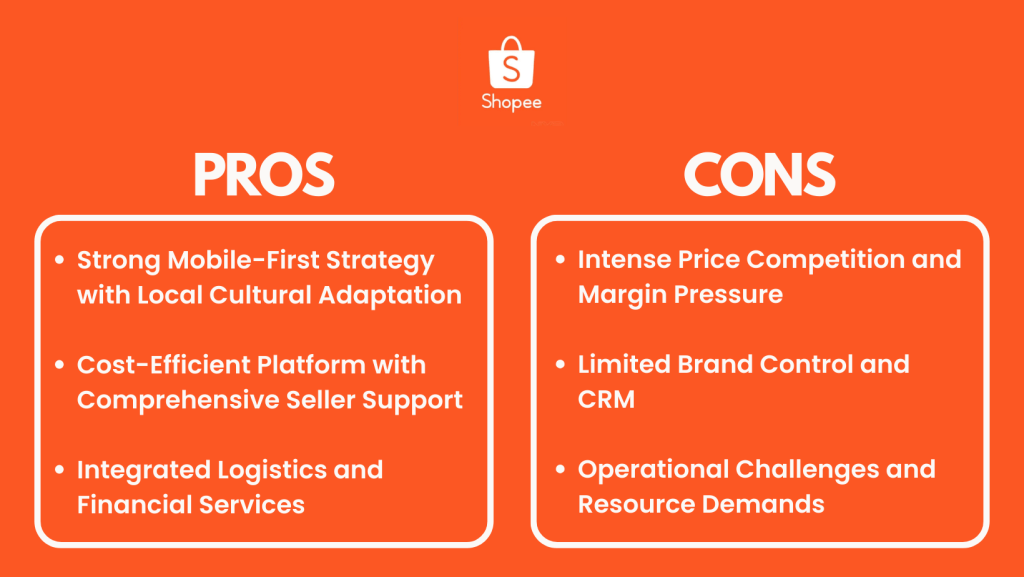
Shopee: Pros and Cons
Pros
1. Strong Mobile-First Strategy with Local Cultural Adaptation
Shopee’s mobile-centric approach and cultural adaptation make it a dominant platform for mobile commerce in Singapore and Southeast Asia.
- Mobile-Centric Platform: Shopee’s mobile app is highly optimized for the Singapore market, reflecting the country’s high smartphone penetration rate (over 90% as of 2021). Features like Shopee Live, in-app games, and social sharing are tailored for mobile users, enhancing engagement and sales. The app’s intuitive interface caters to Singapore’s tech-savvy population, making it easy for all age groups to navigate and transact.
- Cultural Localization: Shopee adapts its platform and marketing efforts to align with local Singaporean and regional cultures and shopping festivals. Celebrates local events monthly, like National Day with themed sales and promotions, resonating with Singaporean consumers. Regular site-wide events like 9.9, 11.11, and 12.12 sales are easy to set up as all you need to do is ‘Nominate’ products and Shopee will handle the rest.
- Shopee Live allows Singapore sellers to host live-streaming sessions, tapping into the growing trend of live commerce. In-app games and Shopee Coins incentivize user engagement and repeat purchases, which is particularly effective in the gamification-loving Singaporean market.
2. Cost-Efficient Platform with Comprehensive Seller Support
Shopee offers a cost-effective entry point for Singapore sellers, coupled with robust support systems to help them succeed.
- Competitive Fee Structure: No fixed monthly fees, making it accessible for small Singapore businesses and new entrepreneurs. Commission rates are generally lower compared to other marketplaces, typically ranging from 1% to 5% depending on the category. Generally Shopee will take a ‘Shipping Subtotal’ and ‘Fees & Charges’ cut, totaling 9% on average for every local transaction.
- Flexible Advertising Options: While basic listing is free, Shopee offers various paid advertising options to boost visibility. As of the second half of 2024, Shopee shops can now advertise on Facebook Ads using existing Shopee product details. This is called the Facebook Collaborative Ads (FB CPAS) and large brands including Microsoft have tried it.

- Comprehensive Seller Education and Support: Shopee University offers free training programs tailored for Singapore sellers, covering topics from basic operations to advanced marketing strategies. Shopee Seller Centre provides analytics tools and performance insights to help sellers optimize their operations. Local support team in Singapore offers assistance in multiple languages, helping sellers sell easily regionally and resolve issues.
3. Integrated Logistics and Financial Services
Shopee provides a suite of integrated services that simplify operations for Singapore sellers.
- Shopee Logistics Services: Integrated with local logistics providers in Singapore, offering competitive shipping rates. Shopee Supported Logistics (SSL) program simplifies order fulfillment and provides shipping subsidies. Cross-border logistics solutions such as Fulfilled By Shopee (FBS) enable Singapore sellers to easily reach other Southeast Asian markets.
- Financial Services and Tools: Shopee Wallet facilitates easy management of earnings and payouts. Integration with local payment methods like PayNow and bank transfers caters to Singaporean consumers’ preferences. Shopee’s partnership with local banks offers special merchant rates for payment processing, benefiting Singapore sellers.
- Business Insights and Analytics: Provides detailed analytics on sales performance, customer behavior, and market trends. Offers insights specific to the Singapore market, helping sellers make data-driven decisions.
Cons
1. Intense Price Competition and Margin Pressure
The competitive nature of Shopee’s marketplace can challenge profitability for Singapore sellers.
- Race to the Bottom Pricing: Shopee’s deal-centric culture often leads to price wars, particularly in popular categories like electronics and fashion. Singapore’s price-sensitive consumers often use Shopee for bargain hunting, putting pressure on sellers to offer competitive prices.
- Promotional Pressure: Frequent platform-wide sales events (like 9.9, 11.11) often require deep discounts, impacting profit margins. Sellers feel compelled to participate in these events to maintain visibility and sales volume, even at the cost of profitability. The cost of sponsored placements during peak sales periods can be high, further squeezing margins.
- Challenge for Small Sellers: Larger sellers or those with direct supply chains can afford to offer lower prices, making it difficult for smaller Singapore businesses to compete. The need for constant promotions and discounts can be unsustainable for businesses with tighter profit margins or unique, higher-value products.
2. Limited Brand Control and Customer Relationship Management
Shopee’s standardized platform can restrict brand expression and direct customer engagement.
- Standardized Store Design: Limited customization options for store fronts make it challenging for Singapore brands to create a unique brand identity. The uniform product listing format may not adequately showcase unique product features or brand stories. Difficulty in standing out visually among numerous sellers, especially for new or smaller brands.
- Restricted Customer Communication: Direct communication with customers is limited to protect buyer privacy, hindering relationship-building efforts. Inability to collect customer data for remarketing or building a direct mailing list. Challenge in providing personalized customer service, which is often expected in the Singapore market.
- Platform Dependency: Sellers are subject to Shopee’s policies and algorithms, which can change unexpectedly. Success on the platform often requires adherence to Shopee’s promotional calendar, limiting sellers’ ability to implement independent marketing strategies. Risk of account suspension or demotion in search rankings if platform rules are not strictly followed.
3. Operational Challenges and Resource Demands
Successfully managing a Shopee store can be resource-intensive and operationally complex.
- Time-Intensive Management: Constant need to update listings, manage inventory, and respond to customer inquiries to maintain good seller ratings. Participation in live streams and interactive features requires significant time investment. Keeping up with frequent platform updates and policy changes can be demanding, especially for small teams.
- Inventory Management Complexities: Syncing inventory across multiple sales channels (if selling on other platforms) can be challenging. Risk of overselling during flash sales or platform-wide promotions if inventory management is not precise. Need for careful forecasting and stock management to meet Shopee’s delivery time requirements.
- Customer Service Demands: High customer service expectations in the Singapore market require prompt responses and issue resolution. Managing returns and refunds can be time-consuming and potentially costly. Maintaining high ratings is crucial for visibility, putting pressure on sellers to meet or exceed customer expectations consistently.
- Financial Management: Managing cash flow can be challenging due to Shopee’s payment cycles and the need to fund inventory for promotional events. Complexity in accounting and tax management, especially for cross-border sales.
In conclusion, Shopee offers Singapore sellers a mobile-centric platform with strong local market penetration and cost-effective entry. Its integrated logistics and financial services, coupled with comprehensive seller support, can be highly beneficial. However, sellers must navigate intense price competition, limited brand control, and significant operational demands. Success on Shopee requires a strategic approach to pricing, promotion, and operations, balanced against the platform’s strong market presence in Singapore and the broader Southeast Asian region.

Key Considerations for Choosing the Right eCommerce Platform
- Business Goals and Scale
- Target Market and Geographical Reach
- Budget and Financial Considerations
- Brand Control and Customization
- Logistics and Fulfillment Capabilities
- Marketing and Visibility Tools
- Technical Skills and Resources
- Platform Ecosystem and Integrations
- Regulatory Compliance
1. Business Goals and Scale
- Consider your long-term business objectives and growth plans
- Assess whether you need a standalone store or prefer to leverage existing marketplaces
- Evaluate the scalability of each platform as your business expands
Case Study: patchandbagel, a Singapore-based decor & gifts brand, started on marketplaces like Etsy and Shopee before transitioning to a Shopify-powered store to support their rapid growth and international expansion. During a quick chat, they however noted that while Shopify provides less transaction fees and allows reach worldwide, they had higher ROAS (Return On Ad Spend) advertising on Shopee to Singapore-based customers.
2. Target Market and Geographical Reach
- Identify your primary target audience and their preferred shopping platforms
- Consider the geographical markets you want to reach (local, regional, or global)
- Assess each platform’s strength in your target markets (e.g., Shopee and Lazada for Southeast Asia, Amazon for global reach)
Insight: According to a Statista report, Singapore’s eCommerce market is expected to reach US$8.9 billion by 2025, with fashion being the largest segment.
3. Budget and Financial Considerations
- Compare the fee structures of different platforms:
- Shopify: Plans range from US$29 to US$299 per month, plus transaction fees
- Amazon: Professional selling plan at US$39.99 per month, plus referral fees
- Lazada and Shopee: No monthly fees, but commission rates vary by category
- Consider the initial investment required for setup and ongoing operational costs
- Evaluate the potential return on investment based on each platform’s market reach and tools
Tool Tip: Use Shopify’s free profit margin calculator to help estimate your potential earnings across different platforms.
4. Brand Control and Customization
- Determine the level of brand identity and control you require
- Assess the customization options available on each platform
- Consider the balance between marketplace exposure and building a unique brand presence
Case Study:
To maximize marketplace reach in Singapore, Samsung maintains a strong presence on Lazada’s LazMall while also operating its own branded online store.
On LazMall, Samsung leverages Lazada’s “Brand Mega Showcase” feature to create a customized storefront that aligns with their global branding.
This multi-channel strategy allows Samsung to maintain strong brand control while also tapping into Lazada’s vast customer base in Singapore. For smaller electronics brands or new entrants to the Singapore market, this case study demonstrates how to effectively balance brand identity with the reach of established marketplaces.
5. Logistics and Fulfillment Capabilities
- Evaluate the logistics solutions offered by each platform:
- Amazon FBA
- Lazada’s Fulfillment by Lazada (FBL)
- Shopee’s Fulfilled by Shopee (FBS)
- Consider cross-border selling capabilities if you plan to expand regionally or globally
- Assess the integration with local shipping providers in Singapore, such as Ninja Van and SingPost
6. Marketing and Visibility Tools
- Compare the advertising and promotion tools available on each platform
- Assess the effectiveness of these tools for your specific product category
- Consider the costs and potential ROI of marketing features
Tool Tip: Explore Facebook Collaborative Ads (CPAS) integration with Shopee for enhanced marketing reach.
7. Technical Skills and Resources
- Evaluate your team’s technical capabilities and the learning curve for each platform
- Consider the time and resources required to manage operations on different platforms
- Assess the availability of support and training resources for each platform
Resource: Utilize Shopify Academy or Amazon Seller University for free eCommerce training.
8. Platform Ecosystem and Integrations
- Examine the app ecosystems and third-party integrations available for each platform
- Consider how well each platform integrates with your existing business tools and systems
- Assess the potential for omnichannel selling and multi-platform management
Tool Tip: Check out Shopify’s App Store or Amazon’s Marketplace Appstore for a wide range of integrations and tools.
9. Regulatory Compliance
- Ensure the platform helps you comply with Singapore’s e-commerce regulations
- Consider features that assist with:
- GST collection and reporting
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) compliance
- Consumer protection laws
Resource: Refer to the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) for guidelines on e-commerce regulations in Singapore.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision on which eCommerce platform aligns best with your business needs in the Singapore market. Remember that the right choice may involve a combination of platforms or evolve as your business grows and market conditions change.
Expert Tip: Consider starting with a multi-channel approach. For example, you could launch a Shopify store for brand control and direct customer relationships, while also listing products on Lazada or Shopee to tap into their large customer base. This strategy allows you to leverage the strengths of multiple platforms while mitigating their individual limitations.

Conclusion and Next Steps
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, choosing the right eCommerce platform for your business in Singapore is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your success in the digital marketplace.
The landscape of eCommerce in Singapore and Southeast Asia is dynamic, with each platform – Amazon, Shopify, Lazada, and Shopee – offering unique advantages and challenges.
Key Takeaways
- No One-Size-Fits-All Solution: The best platform for your business depends on your specific goals, target market, resources, and long-term strategy.
- Multi-Channel Approach: Many successful businesses in Singapore leverage multiple platforms to maximize reach and minimize risks.
- Balance of Control and Reach: Weigh the trade-offs between having full control over your brand (e.g., with Shopify) and accessing a large, established customer base (e.g., with Lazada or Shopee).
- Operational Considerations: Factor in the operational demands of each platform, including logistics, customer service, and technical requirements.
- Financial Implications: Carefully consider the fee structures, initial investments, and potential returns of each platform.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure your chosen platform(s) can support compliance with Singapore’s eCommerce regulations.
Next Steps
- Assess Your Business Needs:
- Clearly define your business goals, target audience, and available resources.
- Research and Compare:
- Dive deeper into each platform using the information provided in this guide.
- Visit the official websites of Amazon, Shopify, Lazada, and Shopee to explore their latest features and pricing.
- Test the Waters:
- Consider starting with a multi-channel approach to test different platforms.
- Many platforms offer free trials or low-cost entry options. Take advantage of these to get hands-on experience.
- Seek Expert Advice:
- Consult with eCommerce experts or attend workshops offered by marketplaces themselves.
- Seek a complimentary consultation with us at Soodo.
- Join online communities and forums to learn from other Singapore-based sellers’ experiences.
- Plan for Growth:
- Choose a platform or combination of platforms that can scale with your business.
- Consider how your choice aligns with your long-term expansion plans, both within Singapore and internationally.
- Stay Informed:
- The eCommerce landscape is constantly evolving. Subscribe to industry newsletters and follow eCommerce trends in Singapore and Southeast Asia.
- Regularly reassess your platform choice as your business grows and market conditions change.
Remember, the journey of eCommerce success is ongoing. Your initial platform choice is just the beginning. Be prepared to adapt, optimize, and potentially diversify your eCommerce strategy as you grow.
By carefully considering the factors outlined in this guide and following these next steps, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed decision and set your eCommerce venture on the path to success in Singapore’s vibrant digital marketplace.
We wish you the best in your eCommerce endeavors!